Using baseline in a rule - Unexpected increase in # of flows rule example
We want to create a Rule that uses baseline functionality. For this purpose, we will analyze the rule implemented in the system by default - Unexpected increase in # of flows rule. It detects an unexpected increase in the number of flows based on the baseline for the last hour.
Implementation
Rules are created and edited in the menu [Alerts>Rules Set]. After entering the tab, in the search field (upper right corner of the window), type the name of the Unexpected increase in # of flows, and click enter key.
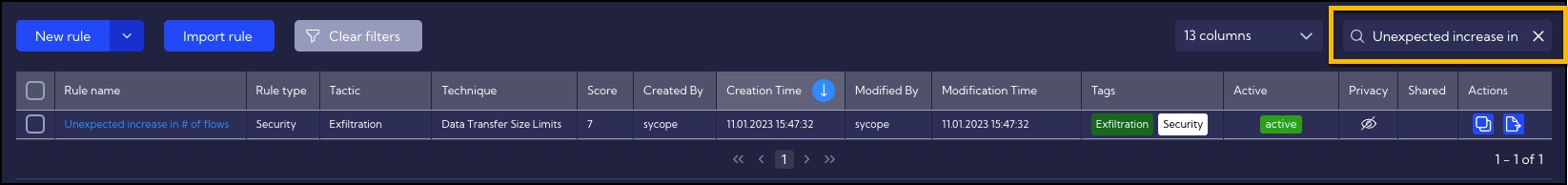
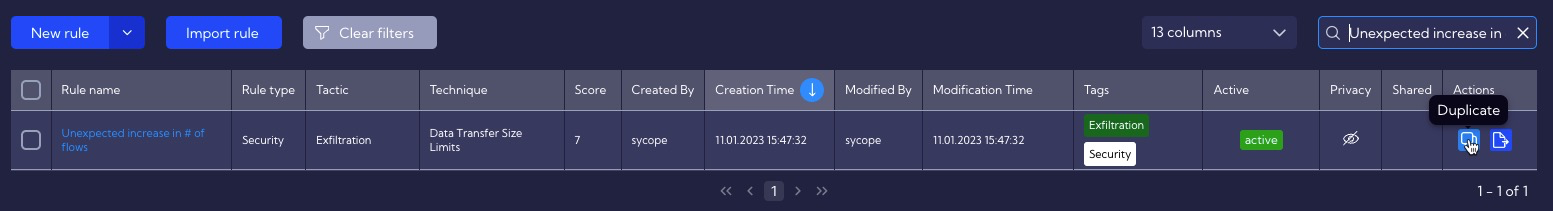
Then you can duplicate the Unexpected increase in # of flows rule so that it can be edited. To do this, use the Duplicate icon from the Action column.
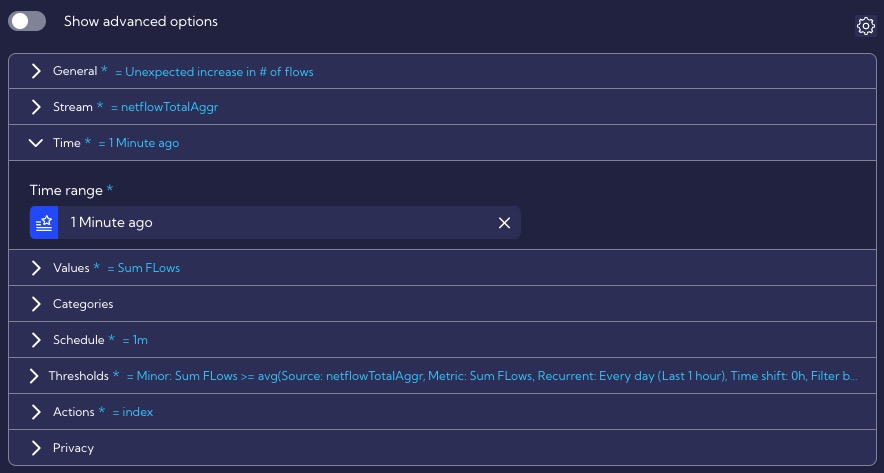
In our case, we want the number of flows in a given minute to be compared with the average of the last hour, so the initial configuration settings look like the following:
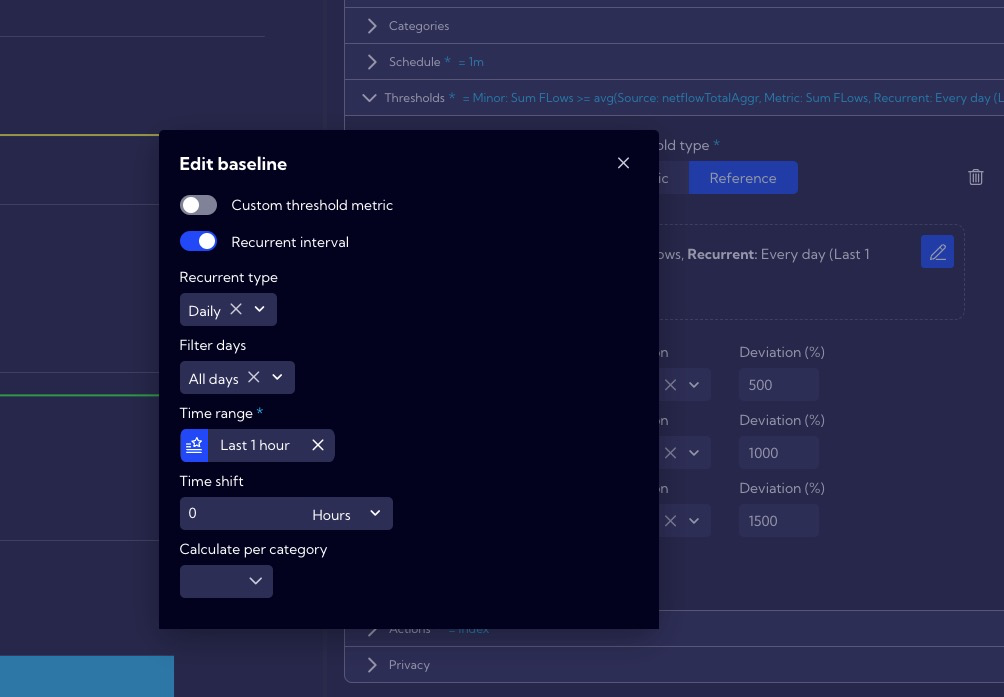
Baselines requirements and recommendations
Objects using baseline functionality (widget, rules) should use an aggregate stream.
If you are analyzing data for a longer period of time, you need to configure data retention for individual streams accordingly. Otherwise, the data will not be available to calculate the baseline.
Configuration of baseline settings is located in the Thresholds section (here, you set the thresholds, after which an alert of the corresponding criticality is triggered).
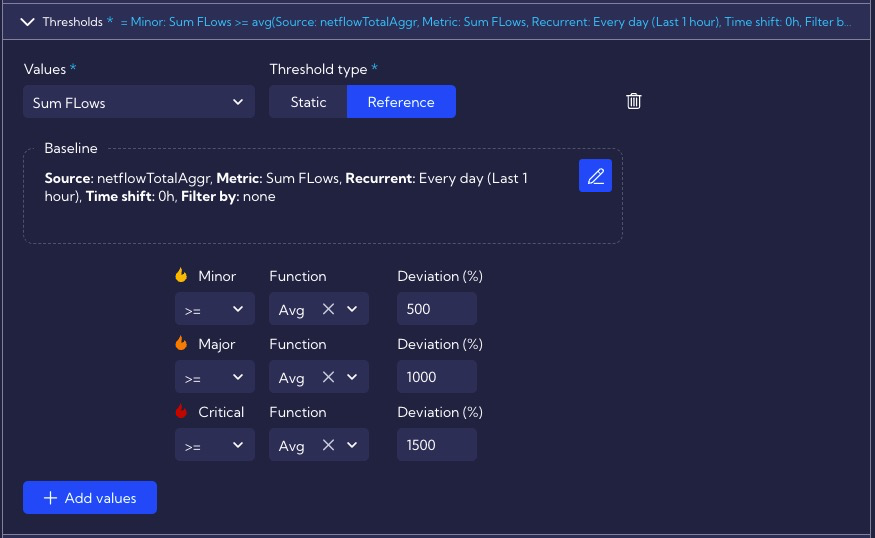
One of the most essential baseline settings is Time Range in the Reference tab (available by pressing the
icon ).